Does Google SEO Affect LLM Optimization? We Analyzed 400+ Keywords to Find Out
AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity are starting to pull searchers away from Google. This shift has marketing teams and brands exploring a new SEO-like acquisition channel: getting mentioned by LLM (Large Language Model) chat tools. Some have even coined this emerging field LLMO, which stands for LLM Optimization. But while Google SEO has […]

AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity are starting to pull searchers away from Google. This shift has marketing teams and brands exploring a new SEO-like acquisition channel: getting mentioned by LLM (Large Language Model) chat tools.
Some have even coined this emerging field LLMO, which stands for LLM Optimization.
But while Google SEO has decades of tested strategies, LLMO — or AI SEO — is still in its early stages of development. Most of us have a general sense that if your name appears in many places online, AI tools are more likely to mention you.
But where exactly do you need to show up, how often, and in what context? For example, how closely does your brand name need to be positioned next to the target keyword you want to rank for?
To shed light on this, we analyzed whether our Google-focused SEO strategy has helped our clients get mentioned by AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity.
Specifically, we wanted to know:
Does ranking on the first page of Google for a specific keyword increase the chances of being mentioned when that keyword is entered into an AI chatbot (e.g., “product development software”)?
Do domain rating and the number of referring domains affect the likelihood of getting mentioned by AI tools?
To answer these questions, we analyzed 400+ bottom-of-funnel keywords across 16 clients of varying sizes, industries (SaaS, services, etc.), and authority levels, all ranking on the first page of Google.
We focused on results from Chat GPT and Perplexity, the most popular AI search tools today, while also briefly covering Claude AI and Google’s AI Overview.
First, we’ll break down the results and share what we learned about how AI tools work, followed by how we set up and executed the study.
We show up 77% of the time in ChatGPT & Perplexity when we rank on the first page of Google
For this study, we took 400+ bottom-of-funnel keywords where our clients ranked on the first page of Google and entered those into ChatGPT and Perplexity.
We then recorded when our clients were mentioned in the AI’s response and when they weren’t. Here’s an example using ourselves (not one of the companies we studied):

Since we focused solely on high-buying-intent keywords — queries indicating the reader was ready to purchase — we weren’t interested in instances where our client was mentioned as a source but not by name in the response.
On average, we found a 72% correlation between our clients ranking on the first page of Google and being mentioned by AI tools. On Perplexity, this correlation is 77%, and on ChatGPT, it’s 67%.

Note: We consider the “the first page of Google” to be the top ten organic spots.
Next, we examined whether ranking in the top three spots on Google for a given term (rather than just the top ten) further increased the likelihood of being mentioned by AI search tools.
The answer is yes. The correlation rises to 72% for ChatGPT and up to 82% for Perplexity.
This means that when our clients rank in the top three positions for a keyword, they are mentioned by AI search engines 77% of the time on average when the user enters the exact same keyword.

It’s particularly interesting that not only is there a strong correlation between ranking in the top ten positions on Google and showing up in AI-powered search engines, but ranking even higher (i.e., in the top three positions on Google) further strengthens that correlation.
What’s causing this correlation? (And what we know about how AI tools work)
All of this begs the question: what’s going on behind the scenes that’s causing this correlation?
On the Google side, we know from decades of SEO research that Google determines the importance and authority of websites through backlinks.
But the key questions are:
How many sites are linking to you?
Who are they?
And who is linking to them?
The more links backlinks you have, especially from authoritative sites, the more authority your site gains. While there are many other ranking factors, current SEO research continues to support the thesis that backlinks are still one of the most important ranking factors.
Another crucial factor is topics: What topics does your site cover? And what topics do the sites linking to you cover? Google evaluates this to ensure relevance when displaying results.
We’re grossly simplifying here, but these two factors (backlinks and topic relevance) help determine which pages Google ranks when a user searches for something.
But what about AI search engines? How do they decide what to recommend or say?
We know that ChatGPT’s web search feature relies on third-party search engines, including Bing:
“To provide relevant responses to your questions, ChatGPT searches based on your prompts and may share disassociated search queries with third-party search providers such as Bing.”
(Source: Open AI help doc)
And, Perplexity’s CEO, Aravind Srinivas, admitted in June of 2024:
“We don’t just rely on our own web crawlers, we rely on third-party web crawlers as well.” (Source)
We also asked Perplexity what it uses to crawl the web in multiple different ways and each time it was some version of what you see in the screenshot below:
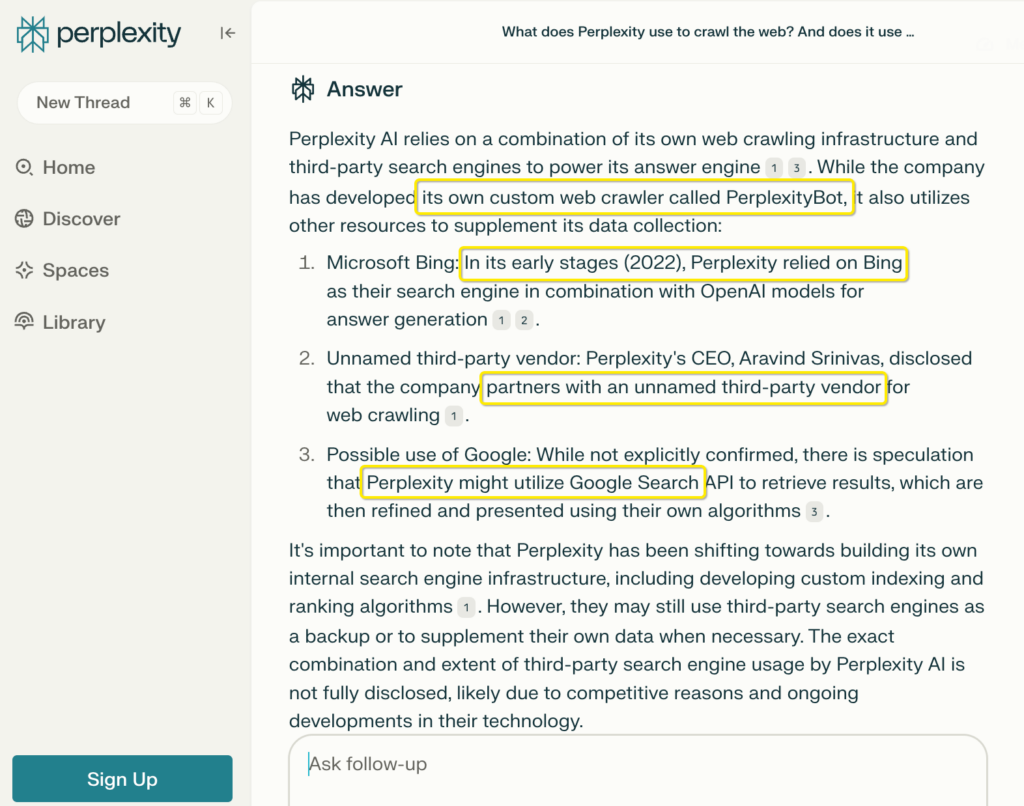
We know both ChatGPT and Perplexity rely on third-party vendors to access current information. While this offers some insight — many marketers assume a strong correlation between search engines like Google and Bing, so ranking on one should help with the other — it’s not the whole picture.
Unlike traditional Google, which only indexes third-party sites, AI tools like ChatGPT also incorporate their training data to craft natural language responses.
This training data comes from a much broader range of sources.

So, how much do these tools rely on their own web crawlers, third-party search engines, or their training data?
We don’t have the full answer, and understandably, OpenAI, Perplexity, Anthropic, and others are somewhat cryptic about their inner workings.
However, the data shows that if our clients rank on Google, they appear in AI search tools for bottom-of-funnel queries up to 77% of the time.
This correlation suggests that, despite the unknowns behind AI’s processes, ranking on Google still plays a significant role in LLMs mentioning you. This is encouraging for brands aiming to boost traffic and leads through traditional SEO and content marketing.
Individual clients saw up to 93% correlation between Google rankings & AI results
Interestingly, when analyzing results at an individual company level, we observed a wide range of correlations, from 0% to as high as 93%.

This raises a key question: Why are there variations? What causes these differences between companies? And can we use this information to determine how a company can optimize its SEO efforts to also get noticed by AI tools like ChatGPT?
We think the answer is yes.
Specifically, we noticed some interesting patterns when analyzing:
A client with a brand-new site and brand ranking only on Perplexity.
A correlation between domain rating and LLM mentions.
A brand-new site seen only by Perplexity and not Google
For example, Client 6 wasn’t mentioned at all by ChatGPT but had a 60% correlation on Perplexity. Why? Client 6 is a young company with a brand-new website and a domain rating of less than 1 when we started working with them in early 2024. It’s likely they weren’t included in ChatGPT’s training data at all.
However, Perplexity operates more like a search engine than an all-purpose AI tool like ChatGPT (you wouldn’t use Perplexity to write a blog post with AI, for instance). It’s possible that perplexity relies less on training data and is more sensitive to what’s ranking in search engines like Google.
When we conducted this study, Client 6 had 11 first-page Google rankings, and we saw their brand name mentioned by Perplexity for 60% of those queries. This suggests that our SEO work and their Google ranking directly influenced their chances of being mentioned by Perplexity.
Domain Rating (DR) and how it affects AI search results
Backlinks play a pivotal role in Google rankings, which is why various SEO tools have developed metrics to measure the quantity and quality of those backlinks. These metrics are referred to as domain authority (Moz), authority score (Semrush) and domain rating (Ahrefs).
In simple terms, the more reputable websites that link to your site, the stronger your website’s authority.
Since LLMs like ChatGPT generate their responses based on common word patterns in conversations, it’s reasonable to assume that they will prioritize the most popular — and thus most linked-to — brands or websites in product discussions or recommendations.
So, we wondered: Does a higher DR correlate with getting mentioned by AI tools?
We used Ahrefs’ domain rating (DR) for this and found that, yes, there is a correlation!

The data above, though sparse, clearly shows a preference for high DR sites being mentioned by ChatGPT and Perplexity. This is significant because higher DR correlates with better SEO rankings, and for years, marketing teams and SEO agencies have focused on improving domain rating through strategies like link building.
If increasing DR helps brands get mentioned by LLMs, we’re in familiar territory.
That said, it’s important to note that this doesn’t mean that AI tools are literally counting backlinks or measuring their strength. More likely, AI tools prioritize websites or brands with strong authority, which might be reflected in their training data or because they base web searches on Google and Bing.
Regardless, this data suggests that continuing to improve DR by creating high-quality content that other websites want to link to is a solid strategy for “ranking” well in LLMs.
Having hundreds of backlinks isn’t the same as having strong website authority
Before moving on, we wanted to dig deeper into the correlation between AI results and backlinks or domain authority.
In addition to analyzing the relationship between DR and AI search results, we also explored how the number of referring domains (i.e., how many unique websites link to yours) correlates with AI mentions.

The slight correlation still exists, but it’s much weaker than the one observed with DR.
This suggests that the raw “number of backlinks” (or referring domains) isn’t the main factor influencing which sites LLMs mention. While the number of referring domains contributes to Ahref’s DR metric, it also factors in the DR of those domains.
It seems LLMs may prioritize site or brand authority similarly, which should reassure brands that have heavily invested in traditional content and SEO strategies.
Setting up the study
For this study, we analyzed 400+ bottom-of-funnel keywords from 16 clients who ranked in Google’s top 10 positions for each search term. The keywords included all three categories of high-buying-intent keywords we typically target: category keywords, jobs-to-be-done, and competitor keywords (i.e., competitor vs competitor, competitor alternatives).
We evaluated results from four tools: ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude AI, and Google’s own AI Overview (more on the last two in the next sections).
Each keyword was entered into the AI tool the same way it would be entered into Google.

Note: We understand that most users chat with LLMs in a more organic way than just entering keywords (e.g., “I need help finding a project management software” vs. “best project management software”). However, we found that that created too many variables. So, for the sake of a controlled study, we simply copied the keyword as-is.
Then, we took note of:
When our client was mentioned. This was marked down as a “Yes”
When other software or services were mentioned, but not our client. This was marked down as a “No”.
When the tool didn’t mention any solutions. For example, sometimes the AI only offered information on the topic (e.g., a definition of project management software) or offered to create the software for you. This was marked down as “N/A”.
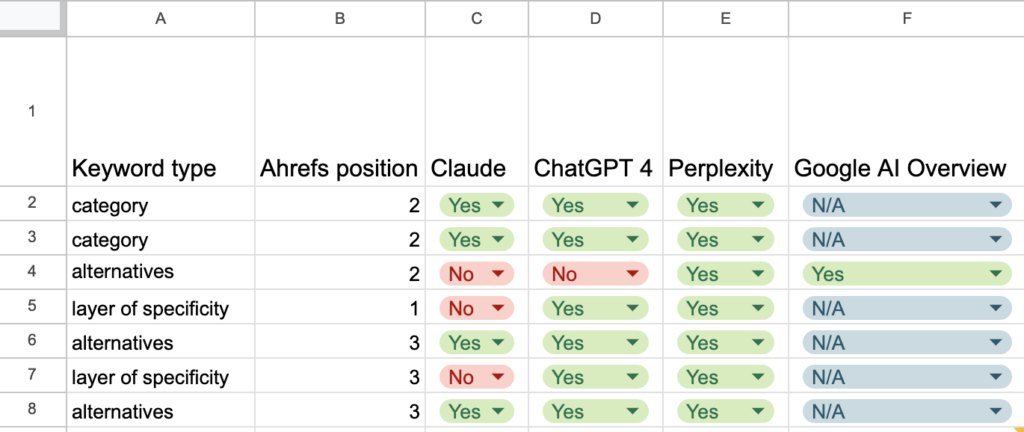
We then calculated the percentage of “Yeses” by dividing the total number of “Yeses” by the combined total of “Yeses” and “Nos.”
As mentioned, all the keywords in this study are bottom-of-funnel queries, meaning the goal is to ultimately sell your product. So, we purposely excluded “N/A” values because no amount of online presence, let alone ranking on the first page of Google, will help if the AI tool doesn’t think the user is looking for a solution. (More on this in a later post.)
As we cover in detail above, we also analyzed results separately for keywords in any position on the first page versus those where we ranked in the top three positions. Additionally, we examined results for individual clients and each tool.

A note on Google’s AI Overview
Marketers and brands have been focused on showing up on AI tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity, but they’re also eager to know how to show up on Google’s AI Overview.

However, this AI Overview isn’t offered for every keyword or for every user. In fact, our study showed that 40% of the time, there was no AI Overview for bottom-of-funnel keywords. Plus, it’s also worth noting that users can choose to turn this feature off.
This means that for most high-buying-intent queries, the reader has to rely on non-AI results (e.g., ads, organic, and sources across the web).
Finally, just because you’re ranking on the first page or even in the top three positions on Google’s SERP doesn’t guarantee you’ll be mentioned by Google’s AI.
Our data shows that if you’re ranking on the first page, there’s only a 31% chance you’ll be mentioned in Google’s AI Overview. And that chance only rises to 43% if you’re in the top three positions.
What’s encouraging is that, in our experience, you can still get plenty of traffic (and potentially leads), if you produce content that ranks well — even when an AI Overview appears above your content.
And, as mentioned earlier, Google’s AI Overview only appears roughly half of the time. So, writing high-quality content that fulfills search intent remains the best way to reach your target audience on Google.
A note on Claude AI
Claude AI is better known as a writing tool than a search engine replacement, and it even admits that it doesn’t search the web — instead, it works off of older training material.

However, we included it in the study for the sake of interest and to confirm that not all tools should be used for search.
And that’s evident from our data. Out of all the tools we tested, Claude had the weakest correlation to Google results by a long shot.

It also had the most “N/A” values of all the tools, as it preferred to create the software rather than list options.

Note: We entered the keyword into Claude just like we would into Google for consistency’s sake, but if we had followed up with Claude and specified that we wanted it a list, it likely would’ve provided one.
So, we wouldn’t spend much effort trying to crack AI tools that weren’t designed for search, as they simply aren’t effective for that purpose.
Instead, we recommend focusing on showing up for tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity. And, as this study showed, continuing with a strong SEO strategy can get you 77% of the way there.
How to work with us or learn more
Work with our agency: If you’d like to discuss how we can work together to create a content strategy that generates leads and possibly increase your chances of getting mentioned by LLMs, feel free to reach out here.
Join our team: If you’re a content marketer or writer interested in this approach to content marketing, we’d love for you to apply to join our team.
Learn our methods in our content marketing course: Individuals looking to learn our agency’s content strategy and become better marketers, consultants, or business owners can join our private course and community, taught via case studies, and presented in both written and video content formats. We include several details and examples not found on this blog. Our course is also built into a community, so people ask questions, start discussions, and share their work in the lesson pages themselves, and we, along with other members, give feedback. Learn more here.























![How To Drive More Conversions With Fewer Clicks [MozCon 2025 Speaker Series]](https://moz.com/images/blog/banners/Mozcon2025_SpeakerBlogHeader_1180x400_RebeccaJackson_London.png?auto=compress,format&fit=crop&dm=1750097440&s=282171eb79ac511caa72821d69580a6e#)

![Brand and SEO Sitting on a Tree: K-I-S-S-I-N-G [Mozcon 2025 Speaker Series]](https://moz.com/images/blog/banners/Mozcon2025_SpeakerBlogHeader_1180x400_LidiaInfante_London.png?auto=compress,format&fit=crop&dm=1749465874&s=56275e60eb1f4363767c42d318c4ef4a#)





















![The 11 Best Landing Page Builder Software Tools [2025]](https://www.growthmarketingpro.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/best-landing-page-software-hero-image-1024x618.png?#)









































![How to Create an SEO Forecast [Free Template Included] — Whiteboard Friday](https://moz.com/images/blog/banners/WBF-SEOForecasting-Blog_Header.png?auto=compress,format&fit=crop&dm=1694010279&s=318ed1d453ed4f230e8e4b50ecee5417#)


























![Brand pitch guide for creators [deck and email templates]](https://blog.hootsuite.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/brand-pitch-template.png)



















![How Marketers Are Using AI for Writing [Survey]](https://www.growandconvert.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/ai-for-writing-1024x682.jpg)